GLP-1
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1(GLP-1) Introduction
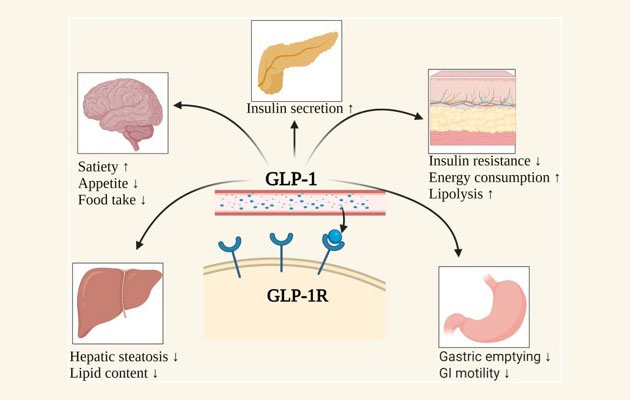
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is classified as an incretin hormone and is secreted by secretory cells (L-cells) in the small intestine.
This hormone plays a crucial role in stimulating insulin secretion after nutrient intake, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Recent studies have revealed the diverse physiological functions of GLP-1, suggesting its potential applications not only in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity but also in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
Currently, GLP-1-based therapeutics are being actively developed as treatments for obesity, suggesting a new treatment paradigm that extends beyond simple blood sugar control agents and encompasses metabolic diseases in general.
PLUTO Inc. is developing a new obesity treatment targeting GLP-1 that maximizes therapeutic effects and enhances the convenience of medication administration.
Obesity
Obesity is a chronic condition characterized by a low energy expenditure compared to the energy consumed, resulting in the accumulation of excess energy in the form of body fat. In other words, it occurs when the amount of activity is insufficient compared to the amount of food consumed. Despite this simple concept, obesity is caused by a complex interplay between various neuroendocrine substances and abnormalities in multiple factors related to energy metabolism. Irregular eating habits, excessive food intake, lack of exercise, endocrine diseases, genetic factors, mental factors, and drugs are the real causes of obesity.
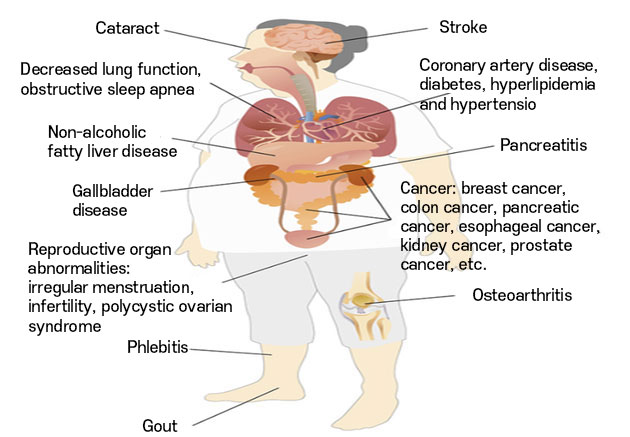
Obesity is not limited to obesity but can be the cause of various diseases and even mental illness. Type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, fatty liver, gallbladder disease, coronary artery disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction), stroke, sleep apnea, gout, osteoarthritis, menstrual irregularities, colon cancer, and breast cancer are representative diseases related to obesity.
